What is dengue?
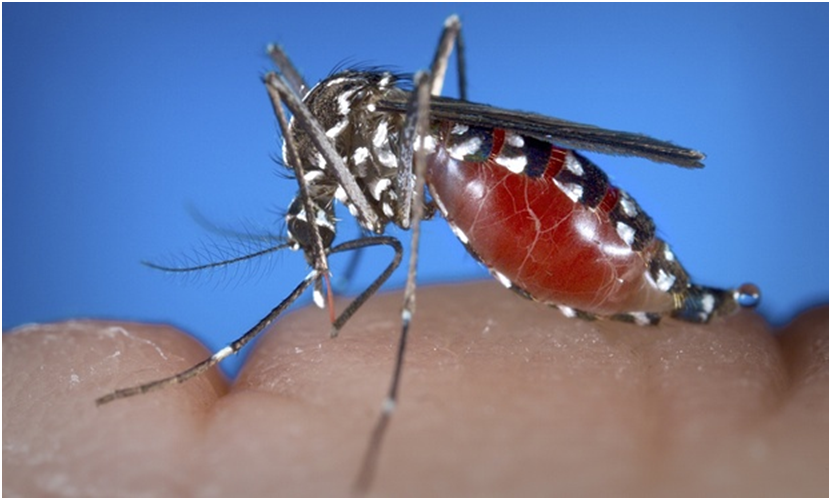
Dengue is a viral infection which is transmitted by biting of an infected female Aedes mosquito. There are four distinct serotypes of the dengue virus (DEN 1, DEN 2, DEN 3 and DEN 4). Symptoms appear in 3–14 days (average 4–7 days) after the infective bite. Dengue fever is a flu-like illness that affects infants, young children and adults.
There is no specific treatment for dengue fever. Severe dengue is a potentially lethal complication but early clinical diagnosis and careful clinical management by experienced physicians can save the life.
How severe dengue is in india?
Dengue was a serious epidemic only in 9 countries before 1970 but now it is endemic in more than 100 countries. Africa ,asia, latin America, united states and Europe…. Dengue has spread two fifth of the global population.
With 19,704 cases reported till September 6, the Dengue cases in the country have already doubled this year. In 2014, the number of dengue cases stood at 10,097, with 37 deaths, through the year. This year, however, 41 people had died.
With 1,259 cases reported so far, Delhi topped the list of cities with the most cases. However, Arunachal’s East Siang district with 1,618 cases (the state has reported 1,681 cases) was the district with highest number of cases, followed by Chittoor in Andhra Pradesh with 761 cases, Thiruvananthapuram (602 cases) and Kasargod (443 cases) in Kerala, respectively. Among cities, Bengaluru reported 1,139 cases, Greater Mumbai reported 306 cases and Kolkata saw 187 cases.The mosquito-borne sickness causes pain so agonising it is also known as “breakbone disease” and last year saw China’s worst outbreak in two decades, with more than 47,000 cases, almost all in Guangdong province
What is dengue mosquito net?
A team of scientists has been driving around a small island in Guaaid Xi Zhiyong of Michigan State University, who heads the ngzhou, southern China, releasing more than half a million mosquitoes from plastic pots on board trucks.this is one of several innovative attempts to tackle dengue fever by diluting the mosquito population with insects that don’t carry this disease..
Xi and his colleagues have worked on this.They released mosquitoes infected with wolbachia bacteria, which make the males sterile and limit the insects’ ability to carry dengue.
Last year’s outbreak has helped persuade residents to embrace the pilot scheme, as has Xi’s willingness to plunge his hand into mosquito pots to prove that the males they are releasing do not bite. And while the Chinese government has not approved the release of genetically modified creatures, it accepted this trial because wolbachia occurs naturally in many insects.
In the first phase, the team aims to reduce the mosquito population, as sterile males breed with wild females. In the second,very fewwolbachia-infected females were released to replace the wild, dengue-transmitting population.
More than half a million specially bred male mosquitoes are being released on an island in southern China every week to fight dengue fever.
The mosquitoes produced at a science park “factory” in Guangdong province can make their female mating partners infertile.
In such a way these Scientists have managed to reduce the number of mosquitoes in some areas of the island by more than 90 percent,
The mosquito “factory” was opened on July 17 and this factory can produce 10 million male mosquitoes every week that are infected with wolbachia, a bacteria that exists widely in many insects, including mosquitoes.
Research shows that eggs produced by mosquitoes that mated with wolbachia-infected male counterparts are infertile.
This will cause a decrease in the number of mosquitoes living in the wild after a certain period.
Between 500,000 and 600,000 mosquitoes are produced every week at the factory and released.
Male mosquitoes released on the island will survive for about two weeks, and their reproduction capacity reaches its peak within the first few days of release.
As a result, the male mosquitoes need to be released on the island continuously to suppress the numbers in the area.
The mosquitoes-only the female bites-are usually released in places with lush plantation, where they are most active.
Conclusion
A team of indian scientist has gone to china to research about this transgenic mosquito and if they found it harmless and effective ,than we may employ the same technique in india also to get rid of dengue.
kanchan Sharma