Difference between FAT 32 & NTFS
FAT (FAT16 and FAT32) and NTFS are two methods for storing data on a hard drive. The hard drive has to either be formatted using one or the other, or can …
Faculty: IT 2019 Sample Papers with Solutions Sr. No. Paper Name Question Paper Link Solution Link 1. Cloud Computing Click Here Click Here 2. Analysis & Design of Algorithm Click Here …
Faculty: IT 2019 Sample Papers with Solutions Sr. No. Paper Name Question Paper Link Solution Link 1. Java Technologies Click Here Click Here 2. Web Technologies Click Here Click Here 3. …
Faculty: IT 2019 Sample Papers with Solutions Sr. No. Paper Name Question Paper Link Solution Link 1. Discrete Mathematics Click Here Click Here 2. Programming in C & C++ Click Here …
Faculty: Science 2019 Sample Papers with Solutions Sr. No. Paper Name Question Paper Link Solution Link 1 Immunology, Virology and Pathogenesis Click Here Click Here 2. Cell Biology Click Here Click …
Faculty: Science 2019 Sample Papers with Solutions Sr. No. Paper Name Question Paper Link Solution Link 1 Plant Biotechnology Click Here Click Here 2. Genetic Engineering Click Here Click Here

FAT (FAT16 and FAT32) and NTFS are two methods for storing data on a hard drive. The hard drive has to either be formatted using one or the other, or can …
FAT (FAT16 and FAT32) and NTFS are two methods for storing data on a hard drive. The hard drive has to either be formatted using one or the other, or can be converted from one to the other (usually FAT to NTFS) using a system tool. FAT32 and NTFS are file systems i.e., a set of logical constructs that an operating system can use to track manage files on a disk volume. Storage hardware cannot be used without a file system, but not all file systems are universally supported by all operating systems.
All operating systems support FAT32 because it is a simple file system and has been around for a really long time. NTFS is more robust and effective than FAT since it makes use of advanced data structures to improve reliability, disk space utilization and overall performance.
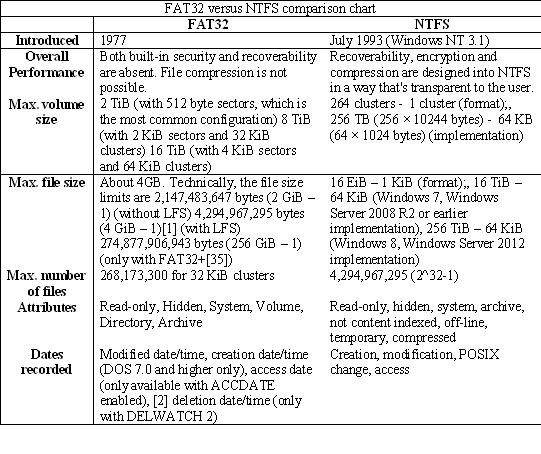
Comparison chart

Simulation is the process of creating an abstract representation (a model) to represent important aspects of the real world. Just as flight simulators have long been used to help expose pilots …
Simulation is the process of creating an abstract representation (a model) to represent important aspects of the real world. Just as flight simulators have long been used to help expose pilots and designers to both routine and unexpected circumstances, simulation models can help you explore the behavior of your system under specified situations. Your simulation model can be used to explore changes and alternatives in a low risk environment. A computer simulation is a simulation, run on a single computer, or a network of computers, to reproduce behavior of a system. The simulation uses an abstract model (a computer model, or a computational model) to simulate the system. imulation software is based on the process of modeling a real phenomenon with a set of mathematical formulas. It is, essentially, a program that allows the user to observe an operation through simulation without actually performing that operation. Simulation software is used widely to design equipment so that the final product will be as close to design specs as possible without expensive in process modification.
Computer simulation in practical contexts
Computer simulations are used in a wide variety of practical contexts, such as:
• analysis of air pollutant dispersion using atmospheric dispersion modeling
• design of complex systems such as aircraft and also logistics systems.
• design of noise barriers to effect roadway noise mitigation
• modeling of application performance[10]
• flight simulators to train pilots
• weather forecasting
• forecasting of risk
• simulation of other computers is emulation.
• forecasting of prices on financial markets (for example Adaptive Modeler)
• behavior of structures (such as buildings and industrial parts) under stress and other conditions
• design of industrial processes, such as chemical processing plants
• strategic management and organizational studies
• reservoir simulation for the petroleum engineering to model the subsurface reservoir
• process engineering simulation tools.

If you’re on the hunt for a new workstation PC or gaming laptop, one of the most important factors to take into consideration is the type of processor. The two most …
If you’re on the hunt for a new workstation PC or gaming laptop, one of the most important factors to take into consideration is the type of processor. The two most common processors used in new models are the Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i7. It may not be clear which processor is right for your needs, especially if you want a general better experience.
Key Differences Between Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i7
Core i7 systems are more expensive than Core i5 systems, usually by several hundred dollars. Core i7 processors have more capabilities than Core i5 CPUs. They are better for multitasking, multimedia tasks, high-end gaming and scientific work. You’ll also find that Core i7-equipped PCs are aimed toward people who want faster systems.
So what are some of the advantages that you can expect to see with the Core i7?
• Faster performance
• Larger cache
• Higher clock speeds
• Hyper-Threading technology
• Integrated graphics
Should You Spend the Money on an Intel Core i7?
First understand how you use your workstation PC. For instance, Hyper-Threading technology (HT) can help a lot with workstation and consumer CPU workloads. Sometimes it doesn’t, but it almost never hurts. If you’re someone who is using your workstation computer for multimedia tasks or running CAD software, then you will benefit from a higher-end processor.
If you use your computer primarily for gaming, HT isn’t necessary. It doesn’t offer a performance boost. That’s not to say that HT will hurt your gaming experience, but don’t expect it to add much either. And while games are getting more CPU heavy, the i5 processors continue to handle them just fine. So if you’re a gamer – even a serious one – a Core i5-equipped system will meet your expectations.
Conclusion
In the end, Intel Core i5 is a great processor that is made for mainstream users who care about performance, speed and graphics. The Core i5 is suitable for most tasks, even heavy gaming. The Intel Core i7 is an even better processor that is made for enthusiasts and high-end users. If you spend your days using CAD software or editing and calculating spreadsheets, the Core i7 will help you accomplish tasks faster.

Customer data come into your organization from every touch point, both physical and virtual—numbers, names, order histories, website preferences. These data are the lifeblood of most organizations today. Like real blood, …
Customer data come into your organization from every touch point, both physical and virtual—numbers, names, order histories, website preferences. These data are the lifeblood of most organizations today. Like real blood, however, data can become contaminated; when that happens, your organization suffers.
Dirty Data Are Pandemic
Inaccurate customer data probably already exist in your system. Experts across industry estimate that inaccurate data affect as many as 22 to 35 percent of businesses in the United States today. Think about the credit card industry. How many times have you received multiple credit card offers from the same company? Do you already have a card with that company? Another example is when a customer calls an organization for support on a product or service. How many times must the customer tell the same story? How many times does the customer service representative on the other end of the line recognize the problem, know what’s been done and what hasn’t, and take the next step without making the customer repeat any of the previous steps?
The problem with these two scenarios is that the customer data are inaccurate in some way. That could mean that they’ve been duplicated across departments that have soloed information that they don’t share. Or maybe the data are incomplete, wrong, or mislabeled. Syntax errors and even typos are common problems with “dirty data.”
Are you’re Data good or Bad?
The problem with bad data is that they can go unnoticed for so long that the damage is done before an organization even realizes that the error has affected sales or customer confidence. Fortunately, one question will help you determine whether you have good or bad data: Do you have data? If you do, then you have bad data. It happens when sales teams key in orders, when a new application is implemented, or when form fields are mislabeled. Bad data happen, and when they do, they can obscure your 360-degree view of your customer.
What you see instead is a fragmented story from which pieces missing. They may even be the wrong pieces altogether. The result can lead to poor customer experiences, which in turn lead to loss of loyalty and confidence. So, yes: Bad data can destroy your customer relationships.
Cleanliness Is Next to Good Customer Relationships
Many organization still use manual cleansing processes to strip out syntax errors, typos, and record fragments in the data they collect, but this is an expensive, time-consuming way to do it. Fortunately, a variety of tools is available to help organizations clean their data and create a holistic view of the customer across the organization. These tools can help organizations build more consistent data sets across all systems, which helps them better understand their customers. Clean, consistent data also make sales teams and customer service representatives more responsive, which means that the whole organization is more agile, and its customer relationships have more depth and meaning.
Don’t misunderstand: Cleaning your data won’t be easy, but it will be worth it. The alternative is a fragmented view of your customer that leads to poor customer experiences, lost sales, and lower profits.

I’m tired of being limited to just DBA_OBJECTS as a test source for exploring a “filtered hierarchy query”. I found out how to generate unique names for each node. Now I …
I’m tired of being limited to just DBA_OBJECTS as a test source for exploring a “filtered hierarchy query”. I found out how to generate unique names for each node. Now I just need to link them up…
The real struggle has been: where to start? I know that’s a vitally important issue based on my earlier experimentation. Vitally important or not, I have to get to the root of the issue..(Snicker; at least until the reality sets in…)
Here’s what I’ve got: the query so far (since I’m using a random number generator, your result sets will almost certainly be different). Here’s what the sub queries do:
1. set the number of records as a parameter.
2. generate the nodes, including the parent ID and name (“T”).
3. chain all the nodes together; this results in lots of records.
4. For each ID, choose the record with the longest chain.
First the SQL, then I’ll discuss the results for two sets of ten (10) records I’m “noodling through”. It doesn’t take a large data set to illustrate the issues.

The last three records look promising: there’s a clear loop-of-3, and one of those is marked as a leaf. So just choose that as the end-point?
No, not quite. The LEAF indicator is unreliable in loops. Look at the third and sixth records. Both are loops-of-1 (with itself), but only one is indicated as a leaf node…
In the first result set (above with the SQL), rows 3 and 5 point to each other. Neither is indicated as a leaf.
I could always “throw out” all the loops, but sometimes that’s a big number of records (not that it’s difficult to generate more). Still I’m wondering how to “break” the loops so they become usable.
Unfortunately, the CSV list of nodes is in different order, so it’s not like it is easy (except visually) to determine that 8,9,10 are together as a loop. Otherwise, I’d just take the maximum number in the loop as the start… or can I? I’d have to parse the numbers… not impossible, but annoying…
राजस्थान का भौतिक स्वरूप अपवाह प्रणाली एवं झीले जलवायु मिट्टी संसाधन

