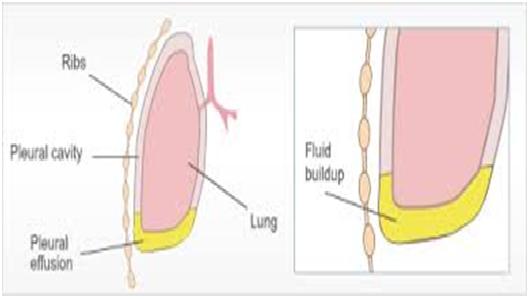
DEFINITION:- It is the collection of fluid in the pleural space. It is a type of primary disorder and due to this secondary sign and symptoms will occur.
TYPES:-
1. Transudate ( Hydrothorax)
2. Exudate
1. Transudate:-
In this type fluid passess through the membranes.
2. Exudate:-
It is a leakage of fluid from the blood vessels into the tissues.
TRANSUDATE occurs in non inflammatory condition. It is a process of accumulation of proteins poor, cell poor fluid which move across intact capilliaries walls. For eg.;- increased hydrostatic pressure in the congestive heart fauilure, decrease onchotic pressure in renal and liver disease.
Accumulation of fluids and cells in an area of inflammation for eg;- Any inflammatory condition , pulmonary malignancies, nephrotic syndrome occurs due to exudate condition.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:-
TRANSUDATE:-
Any alteration in the formation and reabsorbation of pleural; fluid due to imbalance in hydrostatic and onchotic pressure . It has low content of protein & the nature of fluid is clear & pale yellow./
EXUDATE:-
It occurs due to any inflammation and bacterial infection, tumors which causes exudation process . It has a high protein content & fluid is dark yellow & amber.
Pleural effusion
CLINICAL FEATURES:-
1. Pleuritic pain
2. Progressive dyspnea
3.Decreased cheast wall movement
4. fever
5. chills
6. Malignant effusion may result in dyspnea and coughing
7. Malaise
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATIONS:-
1. Physical Examination
2. Pleural biopsy
3. Chest X-ray
4. Pleural fluid analysis
5. C T scan
6. Thoracentesis
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT:-
1. To discusss he underlying cause to prevent reaccumulation of fluid to relief discomfort &dyspnea are the purpose of management including thoracentessis aspiration through syringe.
2. Provide appropriate antibiotics
3. Provide diuretics therapy
NURSING MANAGEMENT:-
1. Take care of patient and prepare him for thoracentesis procedure
2. Reduce the pain by maintain the position &administering analgesics
3. Educate the patient & his family regarding care of drain tube if the client is an out patient.
4. Frequent turning of the patient position will facilitate drainage of the accumulation fluid.