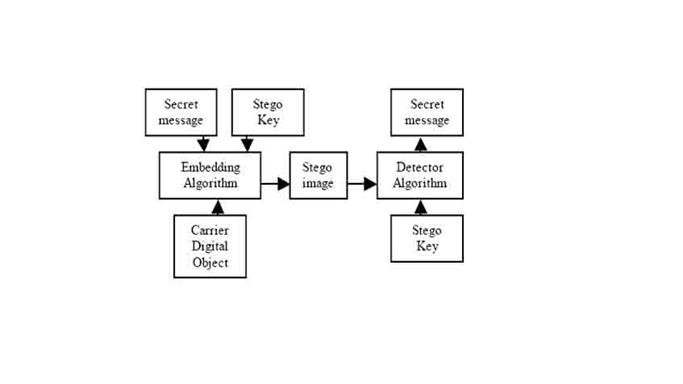
The word steganography comes from the Greek word Steganos, which mean covered or secret and graphy means writing or drawing. Therefore, steganography means, literally, covered writing. Steganography is the art and science of hiding information such that its presence cannot be detected and a communication is happening. Secret information is encoded in a manner such that the very existence of the information is concealed. Paired with existing communication methods, steganography can be used to carry out hidden exchanges. The main goal of steganography is to communicate securely in a completely undetectable manner and to avoid drawing suspicion to the transmission of a hidden data It is not to keep others from knowing the hidden information, but it is to keep others from thinking that the information even exists. The main goal or steganography is to communicate securely in a completely undetectable manner and to avoid drawing suspicion to the transmission of a hidden data]. During the process, characteristics of these methods are to change in the structure and features so as not to images, videos, sound files, and other computer files that contain perceptually irrelevant or redundant information can be used as “covers” or carriers to hide secret messages. After embedding a secret message into the cover-image, a so-called stego-image is obtained. The basic model of steganography consists of Carrier, Message, Embedding algorithm and Stego key. The model for steganography is shown in Figure 1. Carrier is also known as a cover-object, which embeds the message and serves to hide its presence.
Steganography Concept:
Although steganography is an ancient subject, the modern formulation of it is often given in terms of the prisoner’s problem proposed by Simmons, where two inmates wish to communicate in secret to hatch an escape plan. All of their communication passes through a warden who will throw them in solitary confinement should she suspect any covert communication. The warden, who is free to examine all communication exchanged between the inmates, can either be passive or active. A passive warden simply examines the communication to try and determine if it potentially contains secret information. If she suspects a communication to contain hidden information, a passive warden takes note of the detected covert communication, reports this to some outside party and lets the message through without blocking it. An active warden, on the other hand, will try to alter the communication with the suspected hidden information deliberately, in order to remove the information.